Design of Emerge
In this document, we go over some of the design decisions and rationals behind Emerge.
Regular Expression
Language Design
The following features are NOT included in Emerge's Regular Expression language. They seem unnecessary for the purpose of designing and defining tokens of a language.
- Backreference
- Non-capturing group modifier
?: - Lookarounds
?=?!?<=?<! - Anchors:
- Word boundary
\b - Non-word boundary
\B - Start of string only
\A - End of string only
\Z - End of string only (not newline)
\z - Previous match end
\G
- Word boundary
The following features are implemented slightly different in Emerge's Regular Expression language.
- The
.(dot) matches any Unicode character in the range0x00–0x10FFFF, including the newlines.
Parser Design
For building a Lexer from an EBNF input, we need to parse regular expression patterns in the input, so we can construct a DFA for each pattern. To this end, we need to first build a parser for regular expressions.
Building a regex parser is fairly simple and straightforward. Implementing a separate lexer and parser for regular expressions is an inessential complexity (i.e., whitespace characters do not need to be stripped out).
A simple parser for Emerge's regular expressions is built that takes care of terminal symbols. This parser is implemented as a Top-Down Parser using Parser Combinators.
A parser combinator is a higher-order function that accepts a stream of input characters and returns a parsing result. Using a functional programming style, we can implement a context-free grammar (Type-2 language) as a single function that receives an input stream and returns an abstract syntax tree.
We will later use regular expression ASTs to construct DFAs needed for generating a lexer for an EBNF grammar.
Extended Backus-Naur Form
Language Design
The following terminal symbols are removed from Emerge's EBNF language for simplicity and brevity.
- Concatenation (
,) - Termination (
;) - Single quotation (
')
The Solidus (Slash) character (/) is added to Emerge's EBNF language for defining regex patterns.
Lexer Design
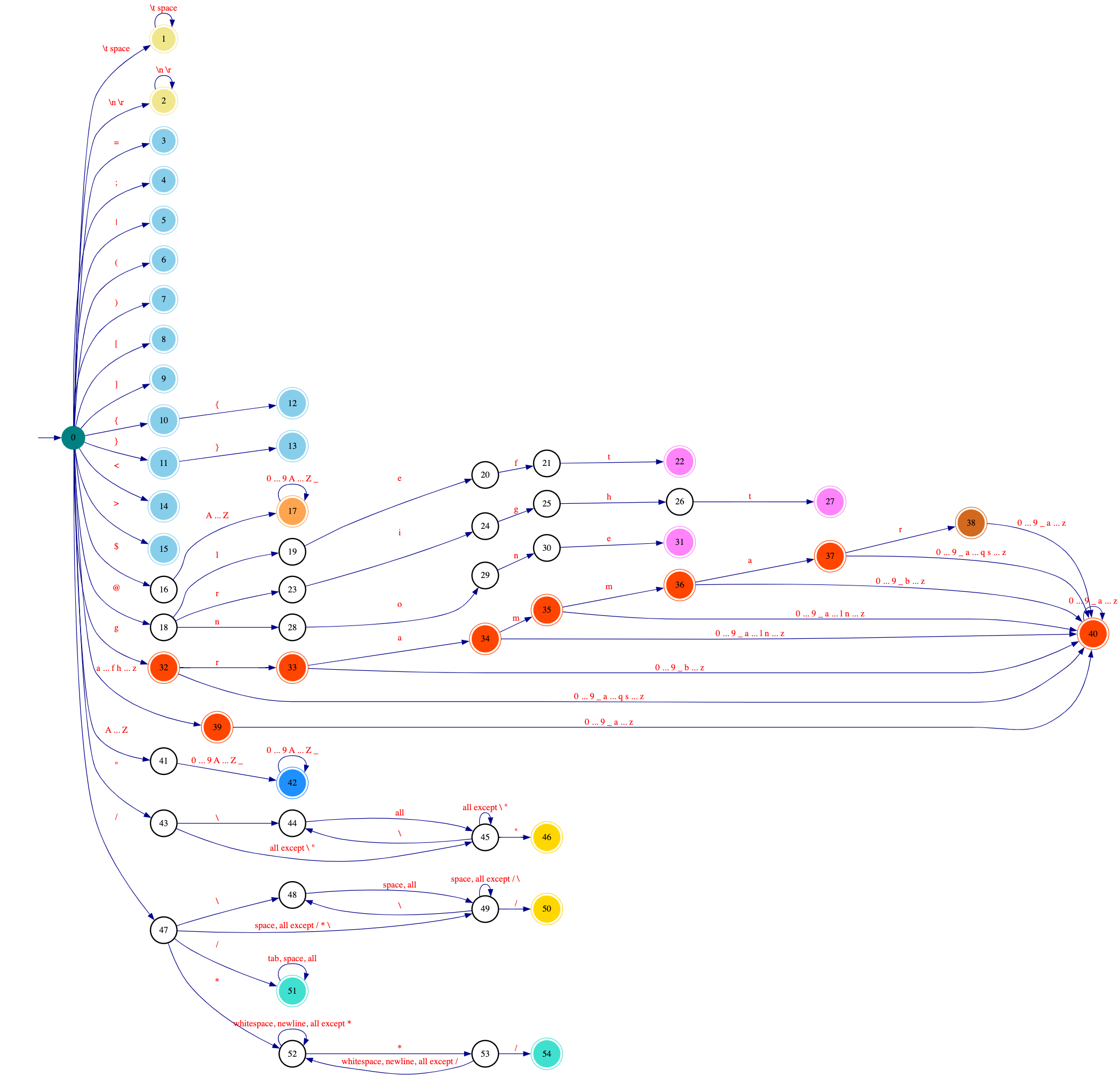
- In the diagram above,
Unicodecovers all characters from0x00to0x10FFFF. - The DFA's final state is evaluated only after encountering an invalid input symbol,
triggering an error for the next state.
- States
10and12are checked only after that invalid symbol, ensuring the DFA correctly distinguishes{from{{. - Likewise, states
11and13are checked only after an invalid symbol, so the DFA correctly recognizes}vs.}}.
- States
- After emitting a lexeme, the DFA resets to state
0. IDENTtokens must start with an uppercase letter (a–z).TOKENtokens must start with a lowercase letter (A–Z).- String constraints:
- The empty string
""is allowed. - The lexer recognizes only these escape sequences:
\\\'\"\t\n\r\x[0-9A-Fa-f]{2}\u[0-9A-Fa-f]{4}\U[0-9A-Fa-f]{8}
- The empty string
- Regular expression constraints:
- The empty regex is not allowed (
//starts a single-line comment). - After a backslash, any character may be escaped (the regex parser later validates which escapes are legal).
- The empty regex is not allowed (
- Comment constraints:
- Empty comments
//and/**/are allowed.
- Empty comments
Lexer DFA Code
digraph "DFA" {
rankdir=LR;
concentrate=false;
node [shape=circle];
edge [color=darkblue fontcolor=red];
start [style=invis];
0 [label="0" shape=circle style=filled color=teal];
1 [label="1" shape=doublecircle style=filled color=khaki];
2 [label="2" shape=doublecircle style=filled color=khaki];
3 [label="3" shape=doublecircle style=filled color=skyblue];
4 [label="4" shape=doublecircle style=filled color=skyblue];
5 [label="5" shape=doublecircle style=filled color=skyblue];
6 [label="6" shape=doublecircle style=filled color=skyblue];
7 [label="7" shape=doublecircle style=filled color=skyblue];
8 [label="8" shape=doublecircle style=filled color=skyblue];
9 [label="9" shape=doublecircle style=filled color=skyblue];
10 [label="10" shape=doublecircle style=filled color=skyblue];
11 [label="11" shape=doublecircle style=filled color=skyblue];
12 [label="12" shape=doublecircle style=filled color=skyblue];
13 [label="13" shape=doublecircle style=filled color=skyblue];
14 [label="14" shape=doublecircle style=filled color=skyblue];
15 [label="15" shape=doublecircle style=filled color=skyblue];
16 [label="16" shape=circle];
17 [label="17" shape=doublecircle style=filled color=tan1];
18 [label="18" shape=circle];
19 [label="19" shape=circle];
20 [label="20" shape=circle];
21 [label="21" shape=circle];
22 [label="22" shape=doublecircle style=filled color=orchid1];
23 [label="23" shape=circle];
24 [label="24" shape=circle];
25 [label="25" shape=circle];
26 [label="26" shape=circle];
27 [label="27" shape=doublecircle style=filled color=orchid1];
28 [label="28" shape=circle];
29 [label="29" shape=circle];
30 [label="30" shape=circle];
31 [label="31" shape=doublecircle style=filled color=orchid1];
32 [label="32" shape=doublecircle style=filled color=orangered];
33 [label="33" shape=doublecircle style=filled color=orangered];
34 [label="34" shape=doublecircle style=filled color=orangered];
35 [label="35" shape=doublecircle style=filled color=orangered];
36 [label="36" shape=doublecircle style=filled color=orangered];
37 [label="37" shape=doublecircle style=filled color=orangered];
38 [label="38" shape=doublecircle style=filled color=chocolate];
39 [label="39" shape=doublecircle style=filled color=orangered];
40 [label="40" shape=doublecircle style=filled color=dodgerblue];
41 [label="41" shape=circle];
42 [label="42" shape=circle];
43 [label="43" shape=circle];
44 [label="44" shape=circle];
45 [label="45" shape=circle];
46 [label="46" shape=circle];
47 [label="47" shape=circle];
48 [label="48" shape=circle];
49 [label="49" shape=circle];
50 [label="50" shape=circle];
51 [label="51" shape=circle];
52 [label="52" shape=circle];
53 [label="53" shape=circle];
54 [label="54" shape=circle];
55 [label="55" shape=circle];
56 [label="56" shape=circle];
57 [label="57" shape=circle];
58 [label="58" shape=circle];
59 [label="59" shape=circle];
60 [label="60" shape=circle];
61 [label="61" shape=doublecircle style=filled color=gold];
62 [label="62" shape=circle];
63 [label="63" shape=circle];
64 [label="64" shape=circle];
65 [label="65" shape=doublecircle style=filled color=gold];
66 [label="66" shape=doublecircle style=filled color=turquoise];
67 [label="67" shape=circle];
68 [label="68" shape=circle];
69 [label="69" shape=doublecircle style=filled color=turquoise];
start -> 0 [];
0 -> 1 [label="\\t, SP"];
0 -> 2 [label="\\n, \\r"];
0 -> 3 [label="="];
0 -> 4 [label=";"];
0 -> 5 [label="|"];
0 -> 6 [label="("];
0 -> 7 [label=")"];
0 -> 8 [label="["];
0 -> 9 [label="]"];
0 -> 10 [label="{"];
0 -> 11 [label="}"];
0 -> 14 [label="<"];
0 -> 15 [label=">"];
0 -> 16 [label="$"];
0 -> 18 [label="@"];
0 -> 32 [label="g"];
0 -> 39 [label="[a..f], [h..z]" color=darkgreen];
0 -> 40 [label="[A..Z]"];
0 -> 41 [label="\""];
0 -> 62 [label="/"];
1 -> 1 [label="\\t, SP"];
2 -> 2 [label="\\n, \\r"];
10 -> 12 [label="{"];
11 -> 13 [label="}"];
16 -> 17 [label="[A..Z]"];
17 -> 17 [label="[0..9], [A..Z], _"];
18 -> 19 [label="l"];
18 -> 23 [label="r"];
18 -> 28 [label="n"];
19 -> 20 [label="e"];
20 -> 21 [label="f"];
21 -> 22 [label="t"];
23 -> 24 [label="i"];
24 -> 25 [label="g"];
25 -> 26 [label="h"];
26 -> 27 [label="t"];
28 -> 29 [label="o"];
29 -> 30 [label="n"];
30 -> 31 [label="e"];
32 -> 33 [label="r"];
32 -> 39 [label="[0..9], _, [a..q], [s..z]" color=darkgreen];
33 -> 34 [label="a"];
33 -> 39 [label="[0..9], _, [b..z]" color=darkgreen];
34 -> 35 [label="m"];
34 -> 39 [label="[0..9], _, [a..l], [n..z]" color=darkgreen];
35 -> 36 [label="m"];
35 -> 39 [label="[0..9], _, [a..l], [n..z]" color=darkgreen];
36 -> 37 [label="a"];
36 -> 39 [label="[0..9], _, [b..z]" color=darkgreen];
37 -> 38 [label="r"];
37 -> 39 [label="[0..9], _, [a..q], [s..z]" color=darkgreen];
38 -> 39 [label="[0..9], _, [a..z]" color=darkgreen];
39 -> 39 [label="[0..9], _, [a..z]" color=darkgreen];
40 -> 40 [label="[0..9], [A..Z], _"];
41 -> 41 [label="All Unicode except \\ \"" color=darkcyan];
41 -> 42 [label="\\" color=darkorange];
41 -> 61 [label="\"" color=darkgreen];
42 -> 43 [label="\", ', \\, n, r, t"];
42 -> 44 [label="x"];
42 -> 47 [label="u"];
42 -> 52 [label="U"];
43 -> 41 [label="All Unicode except \\ \"" color=darkcyan];
43 -> 42 [label="\\" color=darkorange];
43 -> 61 [label="\"" color=darkgreen];
44 -> 45 [label="[0..9], [A..F], [a..f]"];
45 -> 46 [label="[0..9], [A..F], [a..f]"];
46 -> 41 [label="All Unicode except \\ \"" color=darkcyan];
46 -> 42 [label="\\" color=darkorange];
46 -> 61 [label="\"" color=darkgreen];
47 -> 48 [label="[0..9], [A..F], [a..f]"];
48 -> 49 [label="[0..9], [A..F], [a..f]"];
49 -> 50 [label="[0..9], [A..F], [a..f]"];
50 -> 51 [label="[0..9], [A..F], [a..f]"];
51 -> 41 [label="All Unicode except \\ \"" color=darkcyan];
51 -> 42 [label="\\" color=darkorange];
51 -> 61 [label="\"" color=darkgreen];
52 -> 53 [label="[0..9], [A..F], [a..f]"];
53 -> 54 [label="[0..9], [A..F], [a..f]"];
54 -> 55 [label="[0..9], [A..F], [a..f]"];
55 -> 56 [label="[0..9], [A..F], [a..f]"];
56 -> 57 [label="[0..9], [A..F], [a..f]"];
57 -> 58 [label="[0..9], [A..F], [a..f]"];
58 -> 59 [label="[0..9], [A..F], [a..f]"];
59 -> 60 [label="[0..9], [A..F], [a..f]"];
60 -> 41 [label="All Unicode except \\ \"" color=darkcyan];
60 -> 42 [label="\\" color=darkorange];
60 -> 61 [label="\"" color=darkgreen];
62 -> 63 [label="\\" color=darkorange];
62 -> 64 [label="All Unicode except / \\ *" color=darkgreen];
62 -> 66 [label="/"];
62 -> 67 [label="*"];
63 -> 64 [label="All Unicode" color=darkorange];
64 -> 63 [label="\\" color=darkorange];
64 -> 64 [label="All Unicode except / \\" color=darkgreen];
64 -> 65 [label="/"];
66 -> 66 [label="All Unicode except \\n \\v \\f \\r" color=darkgreen];
67 -> 67 [label="All Unicode except *" color=darkgreen];
67 -> 68 [label="*"];
68 -> 67 [label="All Unicode except * /" color=darkgreen];
68 -> 68 [label="*"];
68 -> 69 [label="/"];
}
Input Buffer
A two-buffer scheme, explained here, is employed for implementing the EBNF lexer. The two buffers are implemented as one buffer divided into two halves.
Parser Design
The EBNF parser is implemented as a bottom-up LALR parser, ensuring efficient and deterministic parsing.
The parsing table for EBNF is generated using this algorithm based on the grammar and precedence rules defined here.
To implement an LR parser, the grammar must be in LR(1) form.
LR(1) grammars require minimal transformations, often closely resembling natural language structures.
Ambiguous grammars can also be handled using precedence rules.
Emerge parser generator also produces LALR parsers for the same reasons mentioned above,
balancing efficiency and expressiveness.
For error handling, the panic-mode error recovery method is used due to its simplicity and adaptability to any arbitrary grammar.